Myrtle Rust ‘A Growing Problem’ by Kristy Stevenson
27 September 2022 (6:30pm, for 7:pm start)
Brookfield Hall
Refreshments provided
Myrtle Rust – a growing problem.
Plants from the Myrtaceae family are iconic in the Australian native environment, with gum trees, lilly pillys, tea trees, and paper barks well loved by gardeners and bushwalkers alike. However, over the last few years, you may have noticed a new disease on one of your favourite Myrtaceae plants, the orange/ yellow spores of myrtle rust (Austropuccinia psidii). This short talk with provide some background on the pathogen, it’s history in Australia and impacts so far, in addition to some early results from research undertaken as part of my PhD studies in a wet sclerophyll forest that has experienced high levels of tree mortality due to myrtle rust.
Kristy Stevenson, The University of Queensland
Background:
Kristy is a PhD candidate at the University of Queensland, her research interests are in disturbance and restoration ecology in native forest systems. She completed her undergraduate studies in agricultural science at the University of Tasmania.
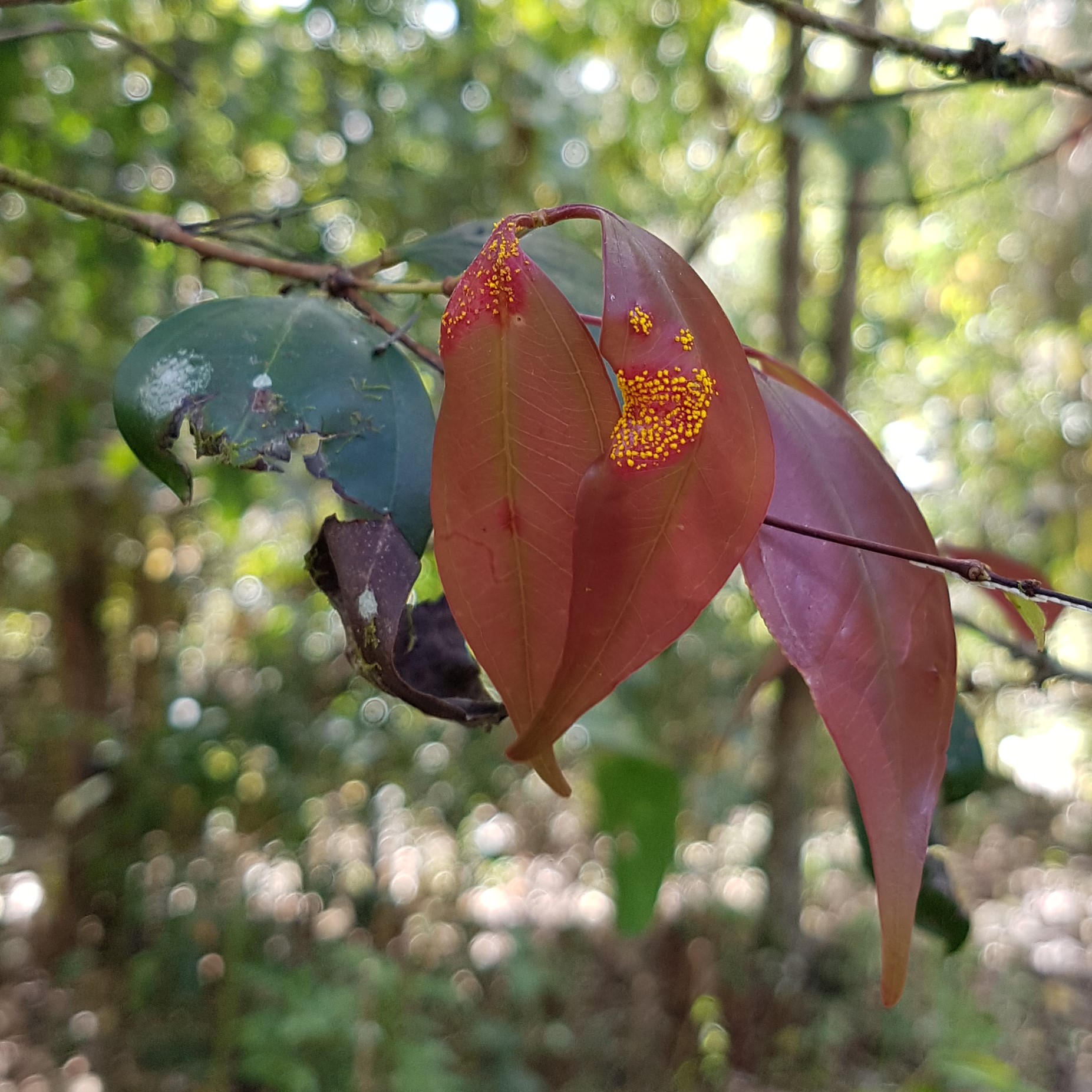

 photo: Ed Frazer
photo: Ed Frazer
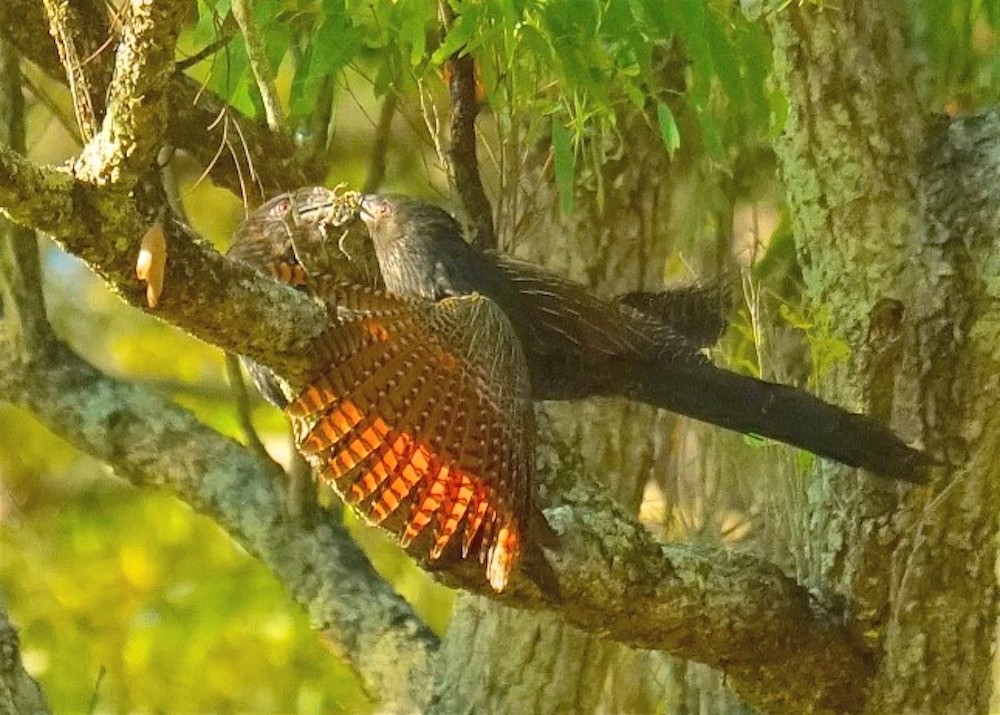






 Pheasant Coucal Photo: Ed Frazer
Pheasant Coucal Photo: Ed Frazer





